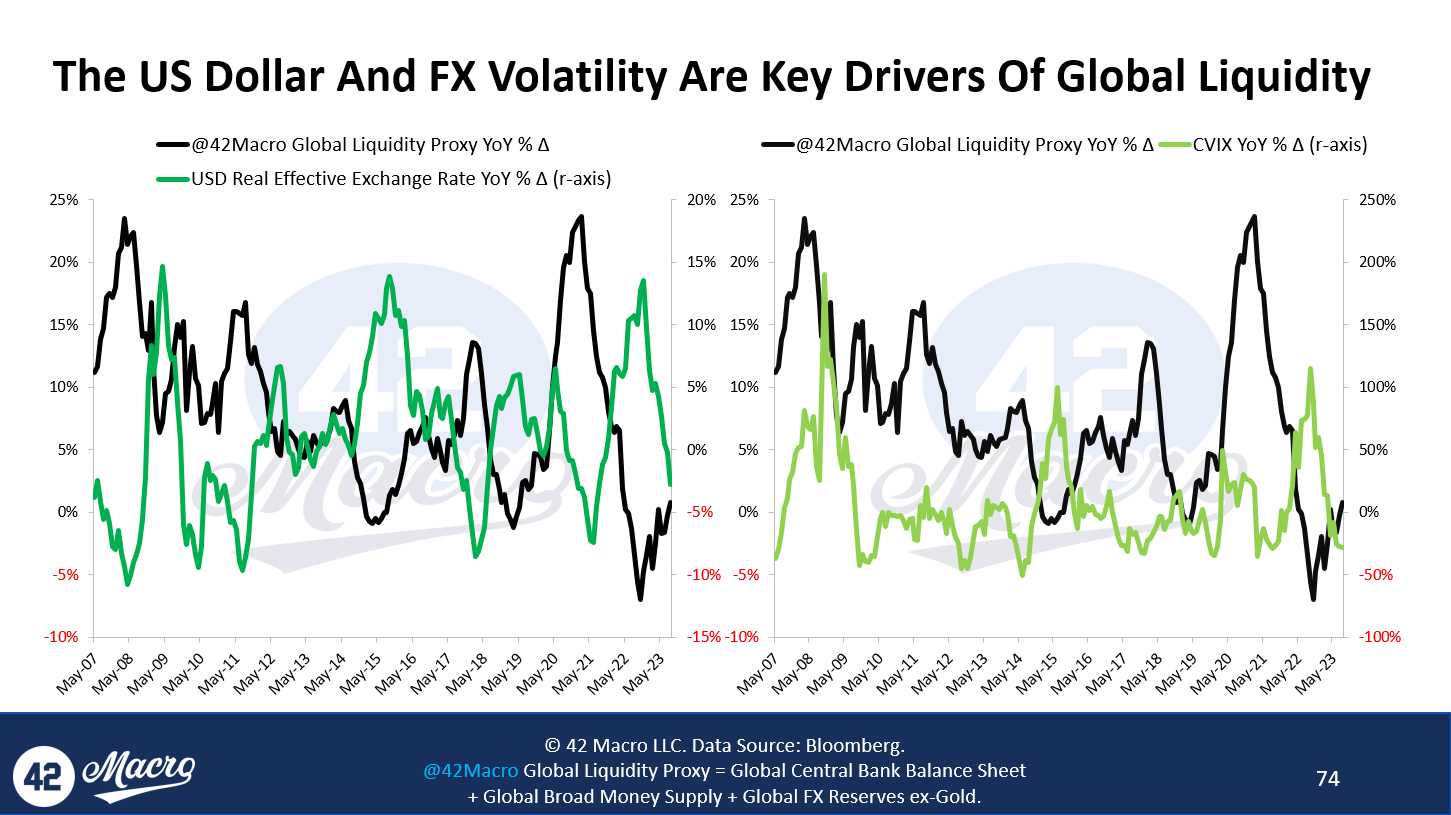
The US Dollar Index is poised for its ninth consecutive weekly advance — the longest winning streak since 2005 as the global currency market rerates economic resiliency in the US and derates the economic outlooks in Europe and China. The reason why FX and interest rate volatility are drags on global liquidity is because when net international investment surplus economies like Japan and the Eurozone see their currencies weaken, it makes it harder for their financial intermediaries to create the dollars required to capitalize investments around the world. FX and interest rate volatility complicate that process and slow down the creation of new dollar supply at the margins.
Growth of the world’s demand for dollars is more stable due to the refinancing requirements of the existing stock of cross-border financing that is denominated in USD — roughly 50% of the total, with ~65% of cross-border loans and ~80% of international debt securities issued by entities that have no organic access to dollars. Thus, fluctuations in the supply of new dollars have an outsized influence in driving FX trends because of the relatively inelastic demand for dollars versus a more elastic dollar supply curve. More FX and interest rate volatility = marginal dollar supply falls faster than marginal dollar demand = stronger dollar. Less FX and interest rate volatility = marginal dollar supply rises faster than marginal dollar demand = weaker USD. This process is reflexive and feeds on itself until exogenous factors like central bank pivots inflect the trend. This is why price momentum in the currency market tends to trend.